Blockchain is a transformative technology that will revolutionize the way information is exchanged across the globe. It stands on the four pillars of Consensus, Provenance, Immutability, and Finality which ensures TRUST in all forms of economic exchanges of value and information. The existence of uncertainty and distrust in all forms of economic exchanges has resulted in tremendous inefficiencies and disruptions between all participants of an economic system, e.g. insufficient trust and information sharing can lead to inefficiency and infectiveness in a bank’s operation as the same information is duplicated across all participants like bank, auditors, regulators, and insurers in the network thus adding costs for their services.
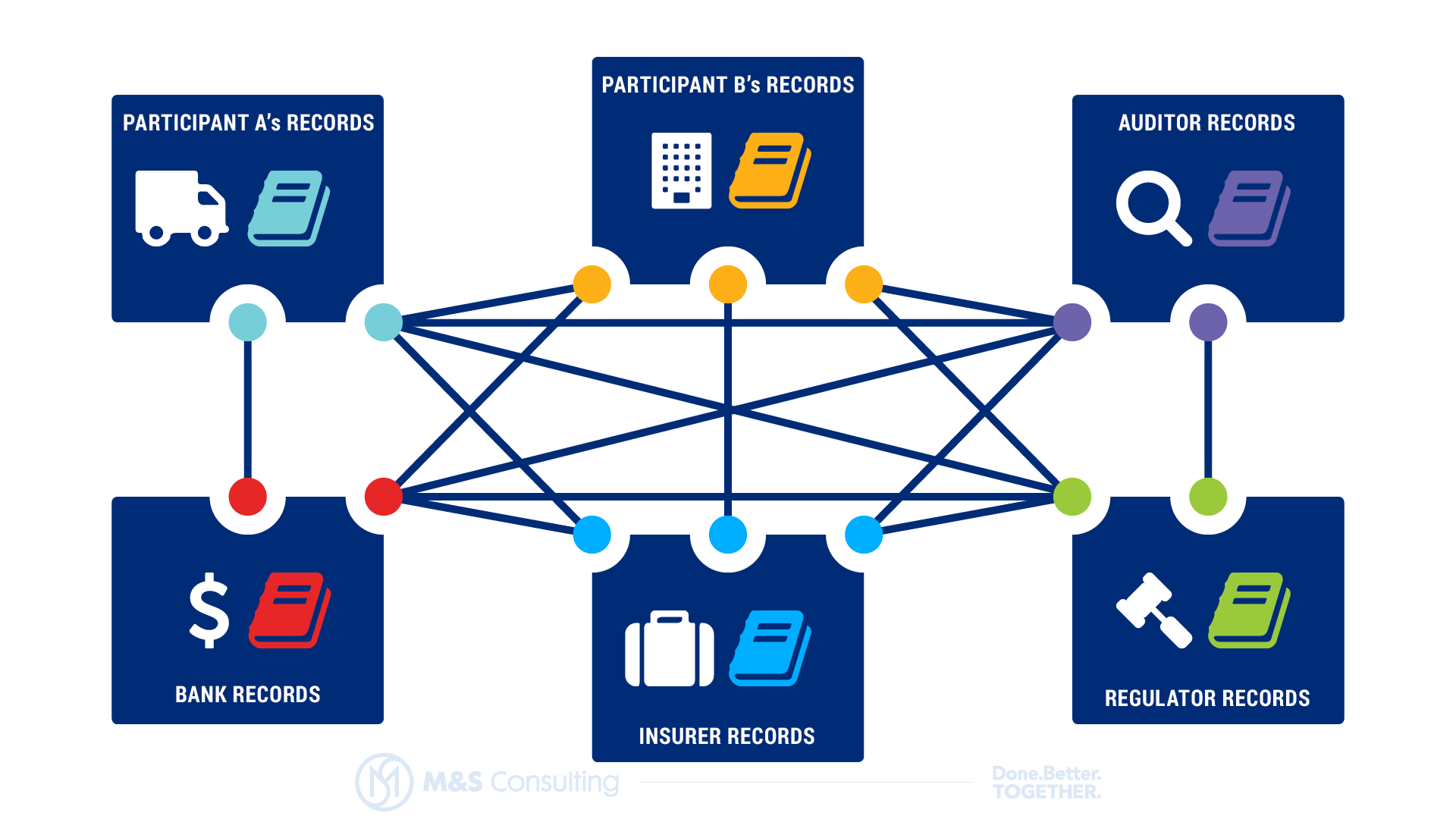
How Blockchain Solves The Inefficiency and Infectiveness Problem
Blockchain provides a shared ledger technology that allows any participant in the network to see the one system of record, with all participants having access to one single decentralized system of records so that business can benefit from a more efficient and transparent exchange of services. This will act like a Wikipedia for business information around assets, contracts, personal information etc., an open, transparent, decentralized, single source of truth without any single controlling authority.
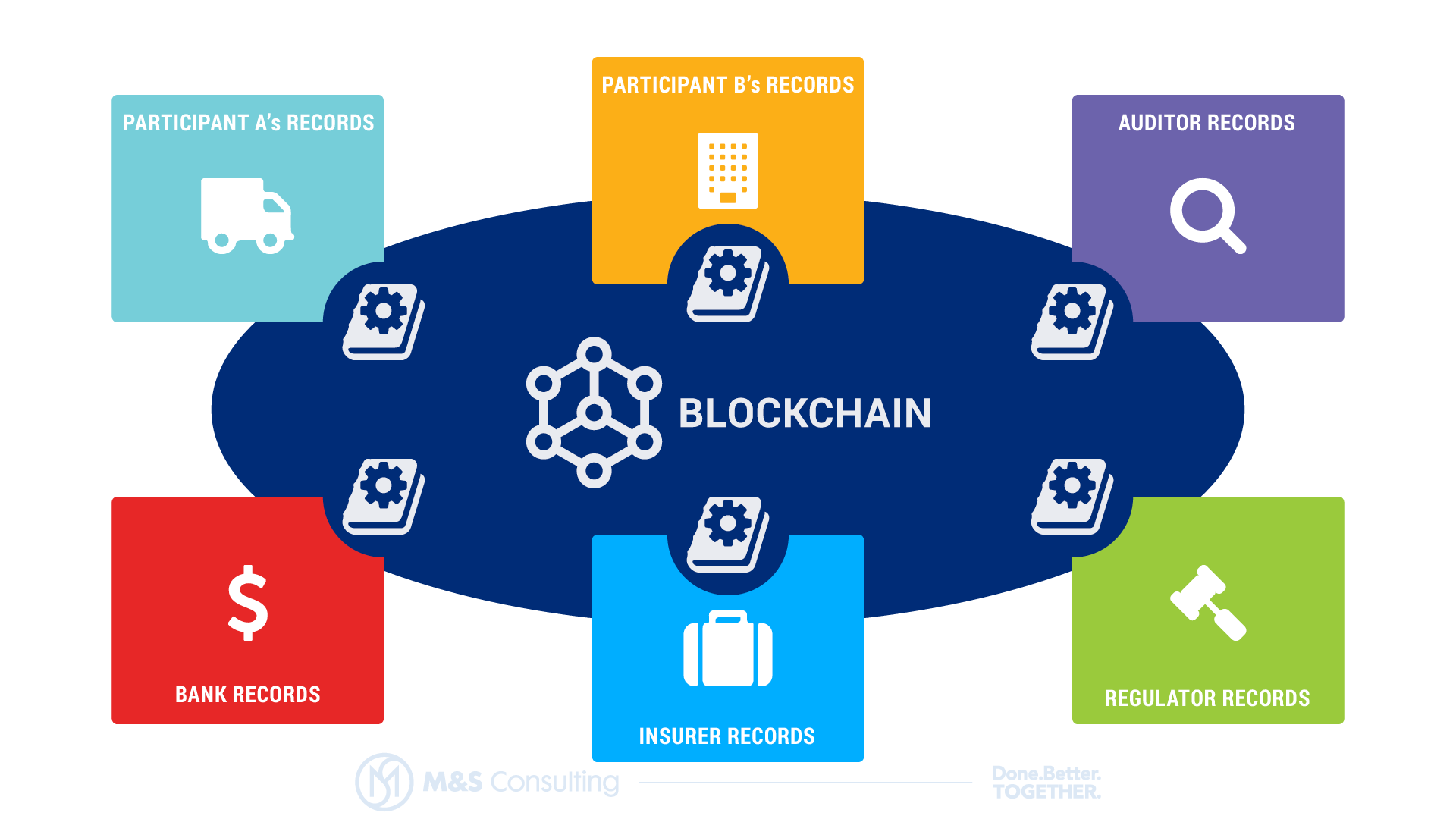
Anatomy of Blockchain
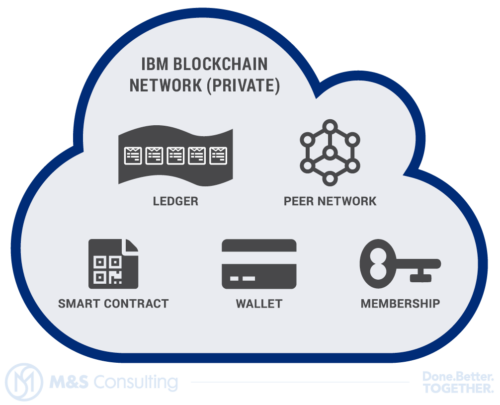
Blockchain is a complex technology that is built on multiple components and technologies working in tandem, behind the scenes, to give the illusion of one single technology product. At its core it has these distinct components:
Shared Ledger
An append-only distributed system of shared records which is maintained by each peer, this is where all the data related to participants and transactions is maintained.
Smart Contract
Automated business rules embedded in the ledger that are executed with an associated transaction. E.g. contract terms under which funds are transferred from one account to another.
Peer Network
A decentralized network of machines that hosts the ledger and smart contracts, each peer on the network play multiple roles in ordering a transaction, executing smart contracts, and validating information.
Membership
Membership services manage the participant identity of all participants and ensure appropriate transaction visibility.
Conclusion
Blockchain is a wonderful technology which holds the potential to become the new world standard of exchanging information after the great internet boom. In the words of the great Steve Jobs, we continue to build solutions using this technology which offers incredible user experiences while keeping the technology invisible to end users.
We would love to talk about how we can help you usher in a new era of TRUST enabled applications and businesses. Use our contact form or give us a call.
